29 Oca
What is Varix?
Son değiştirilme tarihi: 23 Şub 2026
What is Varix?
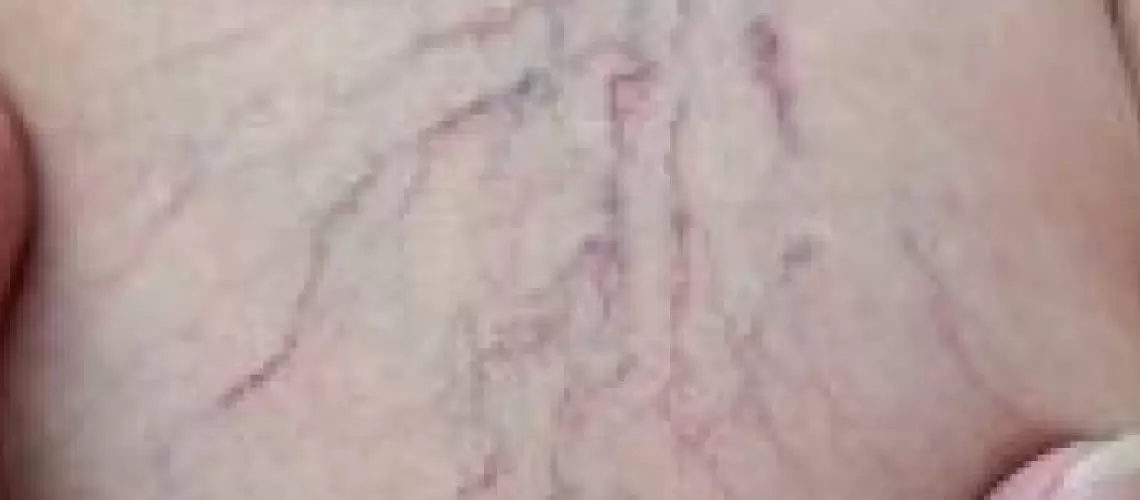
Varix is a severe disease of the veins mostly delayed in treatment as it is generally considered as a cosmetic problem. Initially, it emerges as purplish and greenish vessels on the legs progressing to feet ulcers and cardiac diseases in later stages.
Mechanism of Action
Varix is a problem occurring due to deformation and defunctioning of vein valves in lower extremities. When it becomes impossible to transport dirty blood to lungs, inefficiency occurs with reflux of dirty blood when the patient is particularly in the standing position.
Varices generally occur due to genetic factors or life style influences. The dirty blood accumulating in the lower extremities, in particular, results in edema and swellings. Varices cause some symptoms depending on the size and location of the affected vein.
Symptoms
- Pain in the legs
- Numbness
- Fatigue
- Itching
- Night-time cramps
- Swelling
- Paresthesia
- Restless leg
Types of Varices
Varices are divided into three groups. Different treatment options are available depending on the size and localization of the insufficient vein. Types of varices are as follows:
- Telangiectasias (capillary varices): Generally occur in women in the age group 30 – 50 due to hormonal changes. These superficially-located varices tend to have a diameter under 1 mm. Bluish and reddish in color, telangiectasias are generally not sensed by touching since they are not bulgy in structure. These varices are usually not symptomatic beyond cosmetic problems.
- Reticular (mid-sized varices): These varices can be localized anywhere along the leg but are usually observed behind the knee. Mildly bulgy, reddish and bluish in color, reticular varices should be kept in control.
- Varices of Great Veins: Varices of great veins with diameters above 4 mm are generally bulgy, and visually and/or manually observable. They usually present with major curvatures and are seen in the calves. A major vein that has the potential to grow in time should definitely be treated.
Are There Other Diseases Caused or Triggered By Varices?
Varix is a condition delayed before proper treatment since it becomes manifest in a long time. However the varices occurring due to non-functioning circulatory system and impaired vein valve system present a risk for containing clots inside. The cause of this is slowing down of intravascular blood flow. This condition known as phlebitis presents with complaints including pain, redness and swelling not resolved for a long time.
The clot inside the varix may sometimes reach the vena cava causing deep vein thrombosis, which may lead to very severe problems such as pulmonary embolism.
When not treated or taken under control, varices cause thickening of the skin, swelling in legs, darkening in skin color and wound formations called venous ulcers.
How To Avoid Varices?
Avoiding varices is possible by preserving the health of the circulatory system. The muscles in the legs must be strengthened. To avoid varix formation, it is important to:
- Put the legs up and stretched after long time standing,
- Preserve ideal weight,
- Have a balanced and healthy diet,
- Avoid tight clothes that would hinder blood circulation,
- Consume fiber-rich food to prevent blood pressure from rising,
- Take vitamins A, C and E in a balanced and sufficient diet,
- Follow an exercise program,
- Take little walks after long time in standing position,
- Avoid high-heels.
Related Articles
Minimally Invasive Heart Valve Surgery
Valve diseases are quite common in the society affecting all age groups. There are 4 chambers in the..
Read More
Heart Attack
A heart attack occurs when there is a blockage in the coronary arteries, which are the vessels..
Read More
Coronary Bypass Operations
Heart is composed of a muscular tissue which is pumping blood to the body. Coronary arteries are the..
Read More




